Arthritis is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a joint disorder that causes inflammation, pain, and stiffness, which can limit mobility and make it difficult to perform everyday tasks. There are different types of arthritis, each with its own set of symptoms and causes. In this article, we will discuss the causes and symptoms of arthritis, as well as ways to prevent it.
What is arthritis?
Arthritis is a condition that affects the joints, which are the places where bones come together in the body. It is characterized by pain, inflammation, and stiffness in the joints, which can make it difficult to move and perform everyday activities. There are many types of arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis. Each type has its own set of symptoms and causes. Read here to learn more.
Causes of arthritis
The exact causes of arthritis are not fully understood. However, there are several risk factors that may increase the likelihood of developing the condition. Some of these factors include:
- Age: The risk of developing arthritis increases with age.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop arthritis than men.
- Genetics: Arthritis can run in families.
- Injury: Injuries or trauma to the joints can lead to arthritis.
- Infection: Some infections can cause arthritis.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can put extra strain on the joints, increasing the risk of arthritis.
Symptoms of arthritis
The symptoms of arthritis can vary depending on the type of arthritis and the severity of the condition. However, some common symptoms include:
- Joint pain
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Reduced range of motion
- Redness and warmth around the joint
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Weight loss
Prevention of arthritis
While there is no surefire way to prevent arthritis, there are some steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing the condition. Some of these steps include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can put extra strain on the joints, increasing the risk of arthritis.
- Exercising regularly: Exercise can help strengthen the muscles around the joints, reducing the risk of injury and arthritis.
- Eating a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce inflammation in the body, reducing the risk of arthritis.
- Avoiding injury: Taking steps to prevent injury to the joints can help reduce the risk of arthritis.
- Managing other health conditions: Some health conditions, such as diabetes and high blood pressure, can increase the risk of arthritis. Managing these conditions can help reduce the risk of arthritis.
Treatment of arthritis
While there is no cure for arthritis, there are several treatments available that can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. These treatments include:
- Medications: Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and corticosteroids can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with arthritis.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help improve flexibility and strength, reducing the risk of injury and improving joint function.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace damaged joints.
- Alternative therapies: Alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage, and chiropractic care can also help reduce pain and improve joint function.
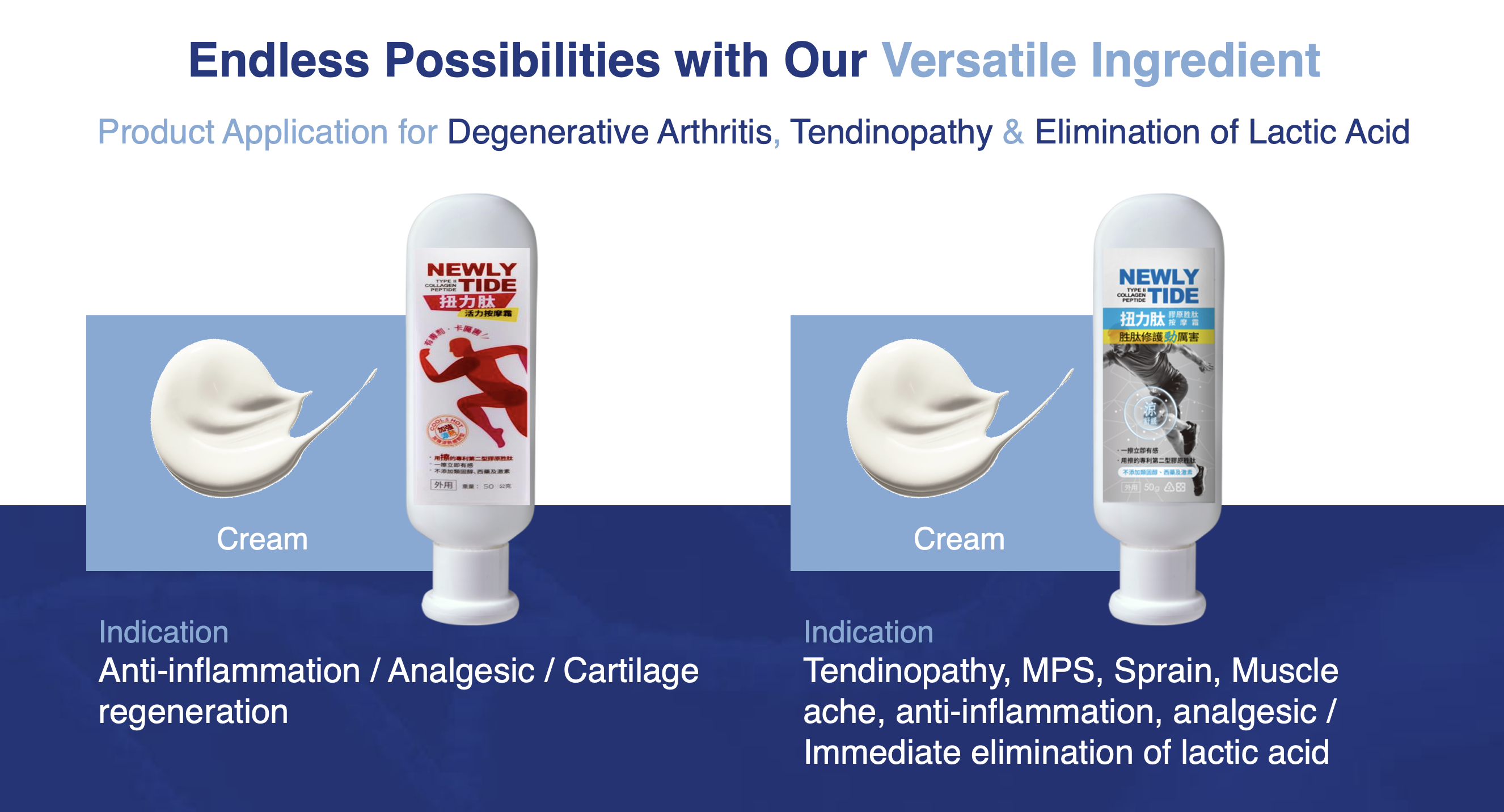
Introducing ICPPX®
ICPPX® is an innovative hexapeptide and pentapeptide targeting degenerative arthritis, tendinopathy, myofascial pain, sprain, and muscle ache, eliminating stasis and subdue swelling. Developed by AHB-Lab patented “Synthetic Biology Peptidomimetic Platform (SBPP)”, ICPPX® may stimulate and activate joint and tendon fibroblasts to synthesize collagen I, collagen II, hyaluronic acid, and fibronectin. It may also have simultaneous anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving effects by decreasing IL-1β and TNFα concentrations in inflamed degenerative arthritis, tendon fasciitis, and ligamentitis tissue.
ICPPX® is produced and refined through fermentation process using endotoxin-free E. coli or edible pharmaceutical grade yeast. The specific ICPPX® peptide were hydrolyzed from the protein by the protease hydrolysis technology and then purified and refined to become high-precision and high-concentration ICPPX® peptide.
ICPPX® Efficacy Studies Highlights
- ICPPX® stimulated the gene expression of type I collagen
- ICPPX® stimulated the gene expression of TGF-β
- ICPPX® stimulated the biosynthesis of collagen and fibronectin
- ICPPX® synergized with TGFβ1 up-regulate ECM biosynthesis
- ICPPX® stimulates procollagen, hyaluronic acid and fibronectin biosynthesis in vivo
- ICPPX® stimulates type II collagen production in human chondrocytes (SW1353)
- Anti-inflammatory Effect of ICPPX® (macrophage H2O2 model)
- Anti-inflammatory Effect of ICPPX® (macrophage NO model)
- Evaluation of TNFα inhibitory activity and cytotoxicity of ICPPX® by in vitro L929 cell proliferation/cytotoxicity assay
- Evaluation of therapeutic efficacy of ICPPX® in rats with degenerative arthritis (Animal Model Design)
If you are looking for a natural remedy to help alleviate arthritis symptoms, ICPPX® may be worth considering. However, it’s important to work with your healthcare provider to determine if ICPPX® is the right choice for you. Together, you can develop a comprehensive treatment plan that will help you manage your arthritis and live a pain-free life. Contact us now for more information!